In the world of metal parts manufacturing, selecting the right CNC machine is one of the most critical choices that affects production efficiency, part precision, and overall business success. For manufacturers focused on high-precision markets like automotive, automation, and machinery building, choosing a CNC system that matches the specific requirements of each project can set apart a reliable operation from a struggling one.
This guide, built on insights from industry-leading sources, provides a systematic approach to choosing the best CNC machines specifically tailored to metal manufacturing, including CNC Milled parts and CNC Turned parts. At CNCRUSH, with over 12 years of experience as a top-tier CNC machining service provider based in China, we have specialized expertise in providing CNC machining solutions that cater to diverse industrial needs globally.
Below, we break down the process of selecting the ideal CNC machine for metal manufacturing across ten essential factors, with detailed insights into each one. Whether you’re scaling up production or optimizing current capabilities, this guide will help refine your choice to maximize production quality and cost-effectiveness.
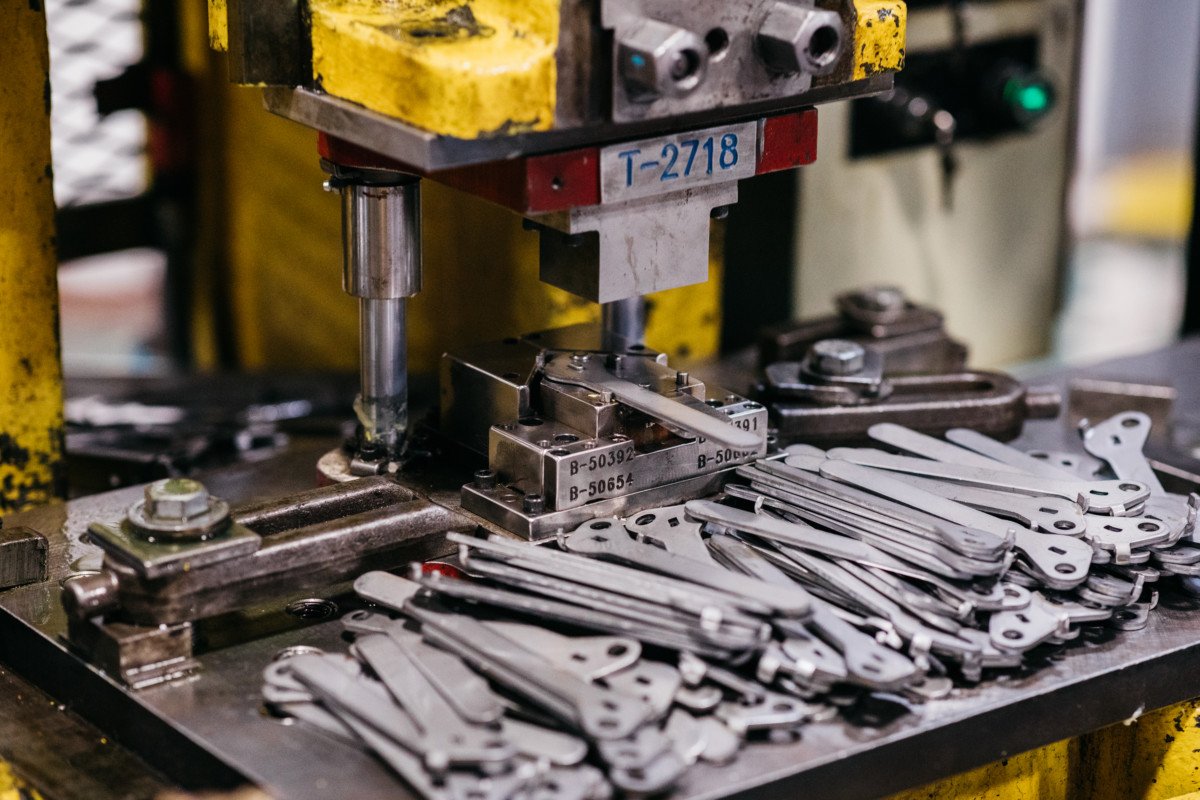

Table of Contents
- Evaluating Material Needs for Metal parts manufacturing
- Understanding CNC Machine Types and Configurations
- Assessing the Complexity of Metal parts
- Choosing Between CNC Milling and CNC Turning for Metal Parts
- Control Systems: The Key to CNC Precision
- Automation and Labor Needs
- Cost Analysis: Budgeting for a CNC Machine
- Maintenance and Downtime Considerations
- Space and Facility Planning for CNC Machinery
- Future-Proofing and Scalability
1. Evaluating Material Needs for Metal parts manufacturing
The material you plan to machine is often the first consideration when selecting a CNC machine. Metals like aluminum, steel, and titanium vary in hardness, density, and machining requirements. CNC machines with higher torque and spindle speed are essential for metals such as stainless steel and titanium, which are harder to cut but necessary for high-stress applications, including automotive and aerospace components.
High-performance machines with stronger spindle motors and robust build quality are critical for such metals. For manufacturers primarily working with softer metals like aluminum, a CNC system with moderate power can suffice but should still offer flexibility for handling tougher materials if production demands change.
2. Understanding CNC Machine Types and Configurations
CNC machines are designed with various configurations to suit specific tasks in metal machining. The most common types are 3-axis, 4-axis, and 5-axis milling machines, each providing different levels of flexibility:
- 3-axis machines are suitable for simpler parts and cost-effective production, though they may lack the sophistication needed for complex geometries.
- 4-axis and 5-axis machines allow for multi-angle milling and turning, ideal for parts with intricate shapes, reducing the need for part repositioning and achieving better precision for complex geometries.
Vertical and horizontal CNC machines each have their benefits, with vertical machines being more cost-effective for smaller parts, while horizontal machines often provide greater stability and faster production for large, heavy components.
3. Assessing the Complexity of Metal parts manufacturing
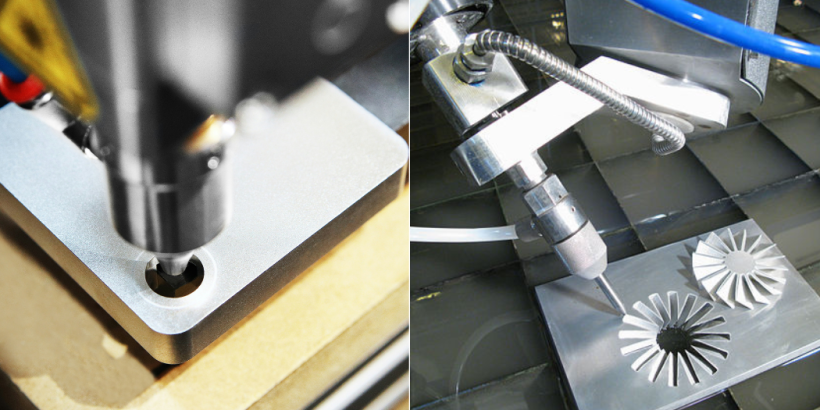
The intricacy of metal parts in sectors like automotive and automation often demands high levels of precision and multiple operations. Choosing a CNC machine based on the complexity of the parts it will produce is essential. Multi-axis CNC machines are ideal for parts with complex shapes, as they allow for simultaneous multi-directional cutting, enabling faster production with fewer repositioning requirements. For businesses requiring mass production of high-precision parts, 5-axis machines can significantly reduce setup time and increase accuracy.
4. Choosing Between CNC Milling and CNC Turning for Metal parts manufacturing
CNC milling and turning are two fundamental machining methods, each suited to different part geometries and production volumes.
- CNC Milling is optimal for creating parts with complex surfaces, contours, and pockets.
- CNC Turning excels at producing cylindrical components like shafts, bushings, and other round metal parts efficiently.
In industries like machine building and automotive, where both flat and round parts are often required, a combination of both milling and turning capabilities can optimize production. At CNCRUSH, we offer both CNC Milled parts and CNC Turned parts to support various industries’ comprehensive production needs.
5. Control Systems: The Key to CNC Precision

CNC control systems, like those provided by Fanuc, Siemens, and Haas, differ in interface, functionality, and support for automated processes. High-end CNC controls often allow for better process automation, intuitive programming, and remote monitoring, which are beneficial for high-volume production. In metal parts manufacturing, control systems that support multi-axis control with high-speed data processing enhance precision and repeatability, a key consideration for sectors like aerospace and medical devices where tolerances are exceptionally tight.
6. Automation and Labor Needs
Automation capabilities in CNC systems can significantly reduce labor dependency, especially beneficial for large-scale production. For example, CNC machines equipped with automatic tool changers (ATCs) and robotic arms can handle more complex operations with minimal human intervention. This setup not only increases efficiency but also reduces operational errors and labor costs. Automated CNC solutions are advantageous for businesses seeking consistency in high-volume production of metal components.
7. Cost Analysis: Budgeting for a CNC Machine
Budgeting for a CNC machine involves evaluating both upfront costs and ongoing operational expenses. While advanced CNC systems with multi-axis capabilities and automation features may have a higher initial cost, they often result in long-term savings by reducing labor and maintenance requirements. Additionally, factoring in the total cost of ownership—including tooling, maintenance, and downtime costs—can help balance immediate investment against operational benefits.
| Cost Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| Initial Machine Purchase | Base cost of the CNC machine |
| Tooling and Fixtures | Cost of tools and setup fixtures |
| Maintenance and Downtime | Regular maintenance costs and unplanned repairs |
| Labor Costs | Operator training and wages |
8. Maintenance and Downtime Considerations
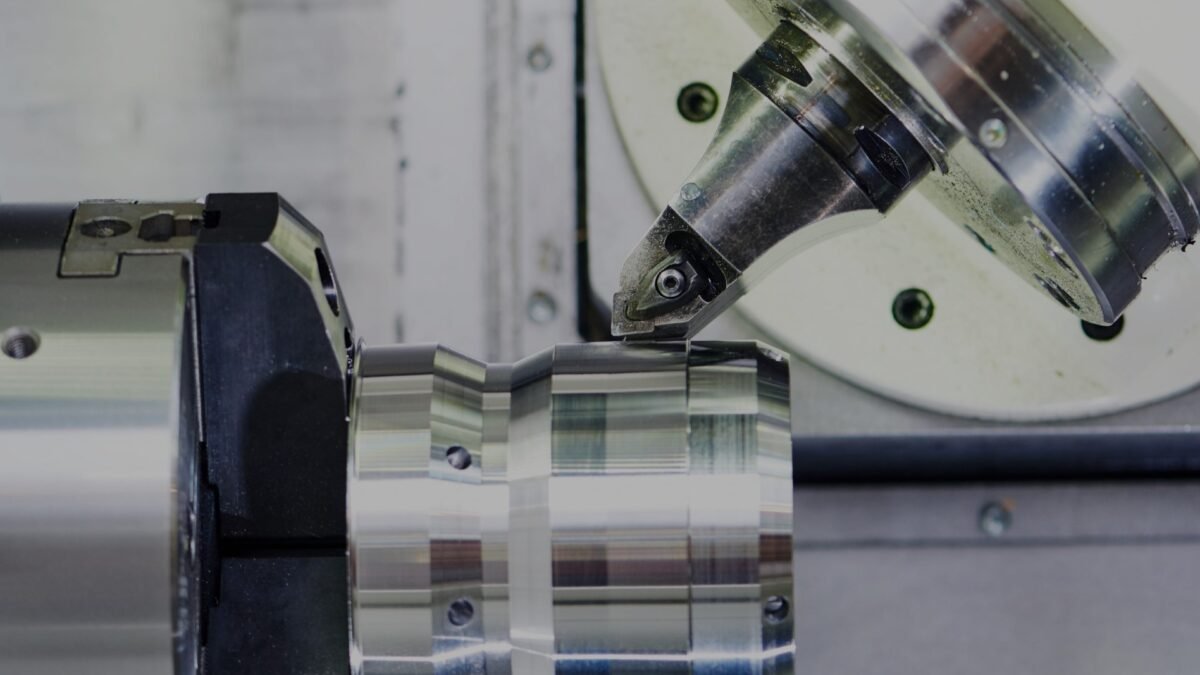
Regular maintenance is crucial to keep CNC machines in optimal working condition, especially when handling hard metals that wear down machine parts faster. Machines that feature built-in diagnostics and easy-access components for repairs are ideal as they reduce downtime. For high-volume production environments, scheduled maintenance programs can minimize unexpected disruptions, ultimately protecting production flow and output quality.
9. Space and Facility Planning for CNC Machinery
The spatial layout and floor space in a manufacturing facility greatly impact CNC machine selection. High-performance machines, particularly those with larger footprints or added automation components, require ample space. Efficient layout planning can enhance productivity by minimizing the movement of parts and materials, improving workflow, and providing safety for operators. Companies should also consider future space needs if additional machines are anticipated.
10. Future-Proofing and Scalability
As market demands and production volumes change, future-proofing your CNC investment ensures that the machine will remain valuable. Machines that can adapt to software upgrades, integrate with new control technologies, or support additional tooling provide flexibility for evolving production needs. Selecting a scalable CNC solution with adaptable software and hardware features can be a cost-effective choice, particularly for businesses looking to expand their metal parts manufacturing capabilities in the future.
FAQs on Choosing CNC Machines for Metal parts manufacturing
Q: What are the most important factors when choosing a CNC machine for metal?
A: Material type, part complexity, machine configuration, and control systems are key. High precision is necessary for complex parts, especially in industries like automotive and aerospace.
Q: How does CNC milling differ from CNC turning?
A: CNC milling is used for complex shapes with contours, while CNC turning is ideal for producing cylindrical shapes efficiently.
Q: Is automation beneficial in CNC Metal parts manufacturing?
A: Yes, automation reduces labor dependency, improves consistency, and lowers operational costs in high-volume production.
Conclusion
Choosing the right CNC machine for metal parts manufacturing is a multi-faceted process, requiring careful consideration of factors like material, part complexity, machine configuration, and control systems. At CNCRUSH, we are committed to delivering high-precision CNC Milled parts and CNC Turned parts through advanced CNC machining services backed by over a decade of experience. As a trusted provider in China, our focus on quality, scalability, and efficiency has made us a reliable partner for industries worldwide in automotive, machine building, and automation. Visit CNCRUSH today to learn more about how our CNC machining services can support your manufacturing needs with precision and professionalism.
