Precision Metal Cutting requires an array of specialized cutting tools to achieve the precision and consistency demanded across industries like automotive, electronics, and aerospace. Each type of CNC tool plays a critical role in shaping metals and other materials, with distinct capabilities that cater to specific applications. Here, we explore the tools that form the backbone of precision metal cutting and highlight best practices for using them in CNC Milled parts and CNC Turned parts production. For over 12 years, CNCRUSH has been a trusted provider of Precision Metal Cutting services, delivering high-quality parts from our facility in China to meet the needs of global clients.
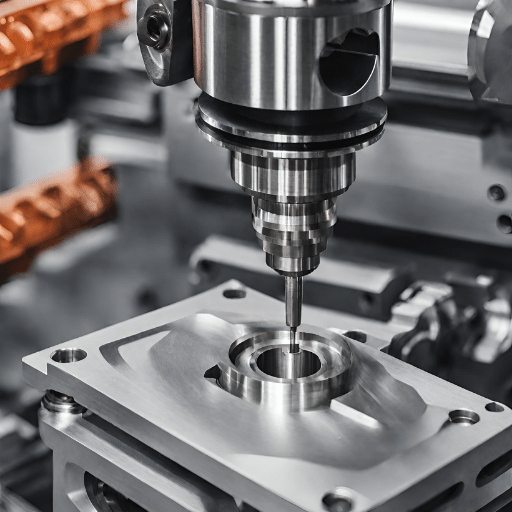
1. End Mills: The Foundation of Precision Metal Cutting
End mills are one of the most versatile CNC tools, widely used in Precision Metal Cutting for creating pockets, slots, and contours. They come in different types like square, ball nose, and bull nose end mills. Square end mills are ideal for sharp-edged cuts, while ball nose end mills are better for creating smooth, rounded edges, often used in mold-making. Bull nose end mills combine flat and rounded features, allowing for precise control over part geometry in applications needing both detail and durability.
2. Face Mills for Surface Finishing
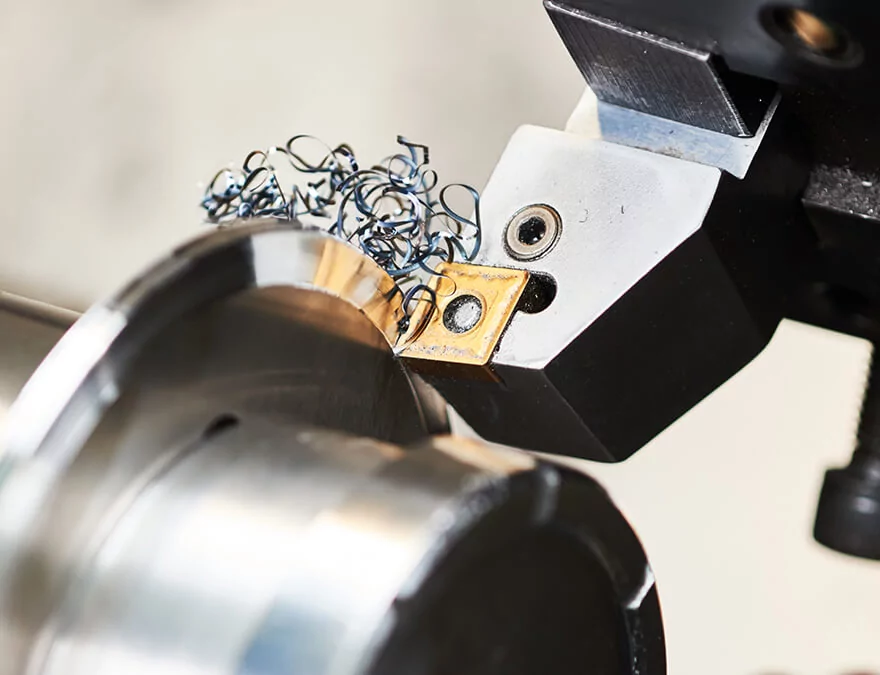

Face mills are critical for creating flat surfaces and fine finishes on large, planar workpieces. These tools remove substantial material in a single pass, which is ideal for operations requiring high productivity and excellent surface quality. The face milling process is often utilized in the automotive and machine building sectors, where uniform finishes are essential for large parts that demand both strength and aesthetic appeal.
3. Drill Bits for Precision Hole-Making
In Precision Metal Cutting, drill bits are fundamental for creating holes of various depths and diameters. From multi-functional twist drills to carbide-tipped models, these tools ensure clean, precise holes that facilitate further processes like threading. CNCRUSH offers CNC Turned parts and drilled components with exact hole tolerances, benefiting industries where precision in connector placement is essential, such as electronics and automation.
4. Reamers for Tighter Tolerances
After initial drilling, reamers are used to refine and expand holes to precise dimensions, ensuring a smooth internal finish and tight tolerances. Reamers play an indispensable role in precision metal cutting, especially in applications requiring exact fit for pins or other cylindrical inserts, making them invaluable for industries like aerospace, where component alignment is critical.
5. Thread Mills for Internal and External Threads
Thread mills create threads with exceptional accuracy, suitable for both internal and external applications. Unlike traditional taps, thread mills can generate threads with only one entry point, improving efficiency and reducing machining time. This capability is particularly valuable in Precision Metal Cutting services for parts that demand complex or variable thread sizes.
6. Gear Cutters for Precision in Rotational Parts
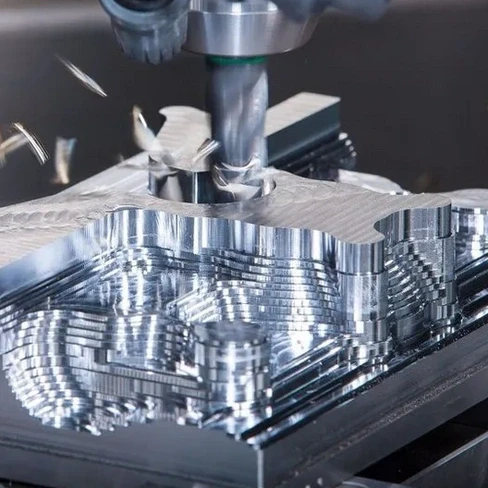

Gear cutters are essential in Precision Metal Cutting gear profiles accurately. These tools are typically utilized in automotive and robotics applications, where gears must meet stringent dimensional and strength requirements. Gear cutters enable precision-cut gear teeth, ensuring that all parts mesh seamlessly within a system.
7. Slab Mills for Horizontal Milling
Slab mills are broad tools, primarily used for creating wide cuts in horizontal milling operations. Their robust design handles substantial material removal, making them ideal for structural components. They are widely used in Precision Metal Cutting parts production for creating deep slots or wide grooves, especially in heavy industries where large parts need to be machined consistently.
8. Hollow Mills for Cylindrical Workpieces
Hollow mills are a specialty tool designed for cylindrical components, with a unique design that revolves around the workpiece to shape it. These tools are suitable for automotive and aerospace applications, where circular shapes like axles or bearings require precise diameters.
9. Chamfer Mills for Angled Edges
Chamfer mills are designed to create beveled edges, enhancing the functionality and aesthetic of machined parts. These mills are commonly used to deburr holes, create angled edges, and improve part finishes. Chamfered edges are essential in machine building and electronics, where smooth transitions are necessary to prevent wear or ease assembly.
10. Slitting Saws for Narrow Cuts
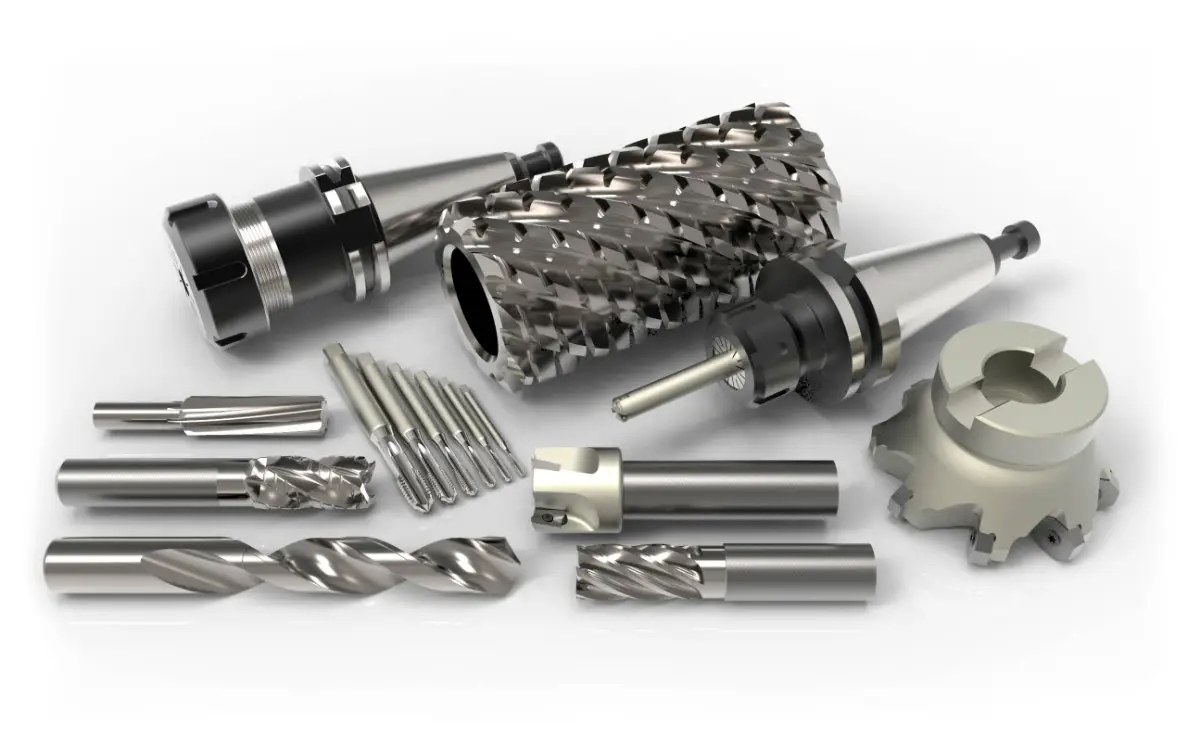

Slitting saws are ideal for making narrow slots and intricate cuts in materials that require minimal disturbance to adjacent surfaces. These saws are commonly used in CNC machining aluminum and CNC machining steel, allowing for fine, detailed work on small components.
| Tool Type | Primary Function | Common Application |
|---|---|---|
| End Mill | Pocketing, Slotting | General milling, mold-making |
| Face Mill | Surface Finishing | Large parts, automotive, machine frames |
| Drill Bit | Hole-Making | Electronics, industrial automation |
| Thread Mill | Threading | Fasteners, connectors |
| Gear Cutter | Gear Tooth Shaping | Automotive, robotics |
Essential Factors in Selecting CNC Tools
Tool Material Selection
Precision Metal Cutting tools are made from various materials, including carbide, cobalt, and high-speed steel. Carbide-tipped tools are highly durable, handling high speeds and maintaining sharpness even in challenging materials. Cobalt and PCD-tipped tools are excellent choices for materials that resist traditional cutters, as their hardness extends tool life significantly.
Workpiece Material and Features
The choice of CNC tools depends greatly on the workpiece material. For example, aluminum may require sharp, high-speed tools with precise coolant control to prevent chipping, while harder materials like steel benefit from robust cutters with superior heat resistance.
FAQ
1. What is the difference between end mills and face mills?
End mills are versatile for creating slots, pockets, and contours, while face mills are designed to produce flat surfaces and smooth finishes on larger areas.
2. How does tool material affect CNC performance?
Tool material influences durability, cutting speed, and overall machining cost. Carbide-tipped and PCD tools typically offer superior performance, particularly for hard materials.
3. Why are thread mills preferred over taps in some applications?
Thread mills allow for versatile thread creation with a single entry point, enabling faster machining of both internal and external threads and reducing tool wear.
Incorporating the right Precision Metal Cutting tools into your CNC machining setup can greatly impact productivity and part quality. CNCRUSH leverages advanced tooling to produce CNC Milled parts and CNC Turned parts with precision, quality, and reliability. With over a decade of expertise, we offer comprehensive CNC machining services to meet the needs of industries like automotive, machine building, and automation. Contact us to learn how our tailored CNC solutions can benefit your projects.
