CNC Turning is a cornerstone of modern manufacturing, enabling the precise production of cylindrical metal parts across industries like automotive, machine building, and automation. This technology has redefined efficiency, accuracy, and scalability, making it indispensable for creating parts ranging from small bushings to complex components for heavy machinery.
At CNCRUSH, we’ve spent over 12 years delivering CNC machining services from our advanced China CNC factory, specializing in high-quality CNC Milled parts and CNC Turned parts. This article provides a deep dive into the essentials of CNC turning, explaining its capabilities, benefits, and applications, while highlighting why choosing expert partners like CNCRUSH ensures optimal results.
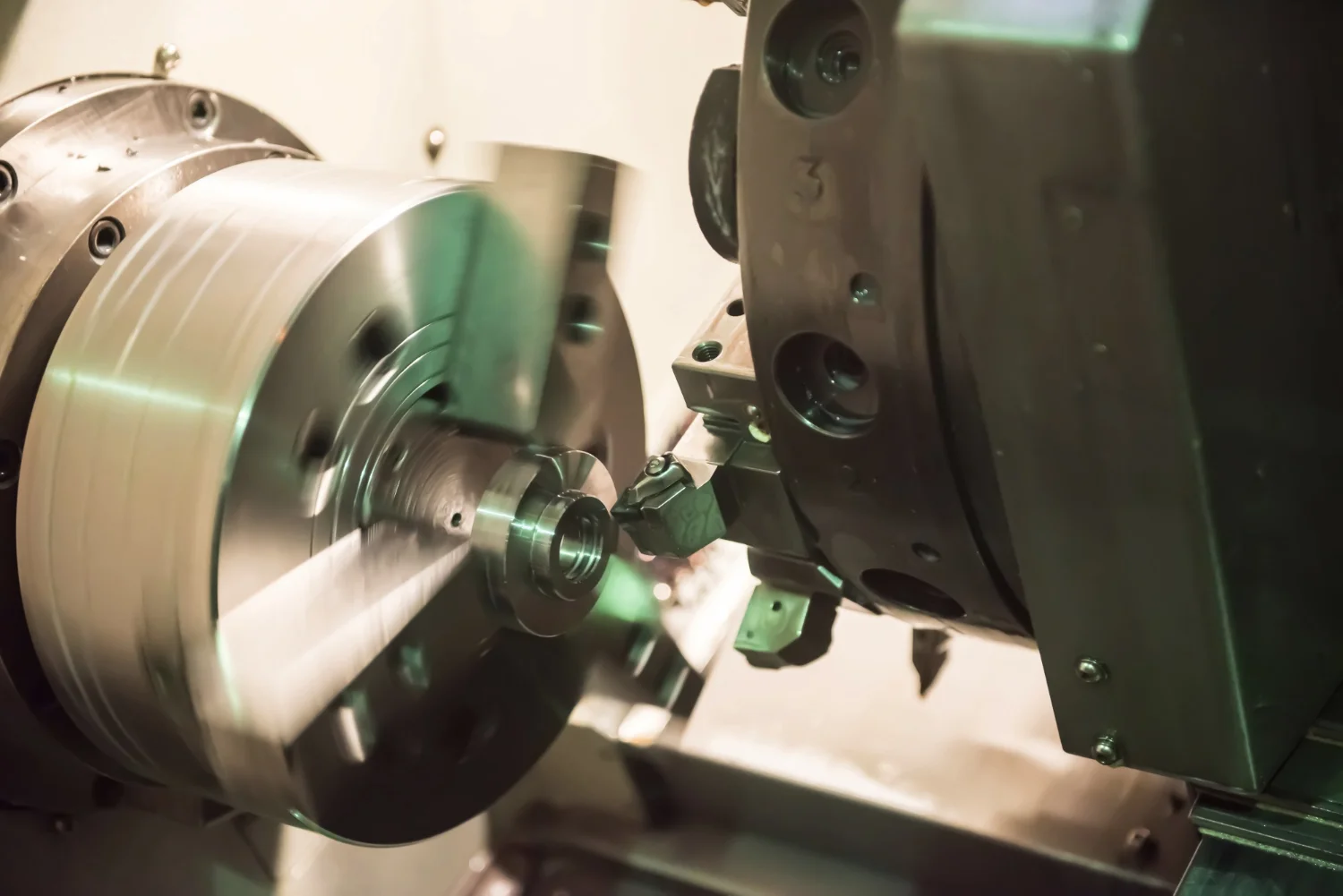

What Is CNC Turning?
CNC Turning is a machining process where a workpiece rotates on a lathe while a cutting tool removes material to create precise, cylindrical shapes. Controlled by computer numerical control (CNC), this process is highly versatile and can handle materials such as aluminum, steel, brass, and even advanced plastics.
| Key Features of CNC Turning | Why It Matters |
|---|---|
| Rotational Symmetry | Ideal for cylindrical parts. |
| High Precision | Achieves tight tolerances of ±0.01 mm. |
| Broad Material Compatibility | From lightweight aluminum to durable steel. |
💡 Did You Know? CNCRUSH uses the latest CNC precision turning technology to craft components with superior surface finishes, perfect for automotive and automation applications.
1. The Fundamentals of CNC Turning Machines
CNC turning relies on lathes, which rotate the workpiece while the cutting tool removes material. Unlike traditional manual lathes, CNC-turned centers automate the entire process, delivering precision and repeatability.
Components of a CNC-Turned Machine:
- Chuck: Holds the workpiece securely.
- Cutting Tool: Shapes the material into the desired geometry.
- Control Panel: Operated via CNC programming for precise movements.
💡 Tip: Choosing the right machine for your production needs—whether for small batch runs or high-volume manufacturing—is critical to achieving optimal results.
2. How CNC Turning Works: Step-by-Step Process
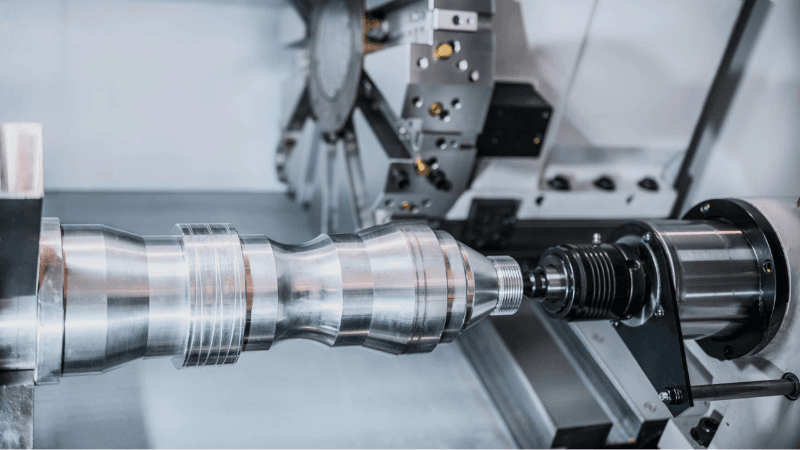
Step 1: Programming
The operator creates a digital toolpath using CAD/CAM software, specifying dimensions, material removal paths, and speeds.
Step 2: Workpiece Setup
The raw material is clamped onto the lathe’s chuck.
Step 3: Material Removal
The cutting tool moves along programmed paths, shaping the material into the desired part.
Step 4: Quality Inspection
After machining, parts are inspected to ensure they meet specifications.
At CNCRUSH, we integrate real-time monitoring during this process, ensuring accuracy and efficiency for every project.
3. Advantages of CNC-Turned Metal Parts
CNC Turning offers a host of benefits over traditional machining methods.
| Advantage | Impact |
|---|---|
| High Precision | Ensures parts meet exact specifications. |
| Speed and Efficiency | Reduces production time for bulk orders. |
| Cost-Effectiveness | Minimizes material waste and labor costs. |
| Versatility | Handles a wide range of materials and geometries. |
4. CNC Turning vs. CNC Milling

While CNC-turned and CNC-Milled share similarities, they differ in execution and applications.
| Feature | CNC Turning | CNC Milling |
|---|---|---|
| Workpiece Movement | Rotates during machining. | Remains stationary. |
| Typical Parts | Cylindrical components like shafts. | Complex geometries like brackets. |
| Production Speed | Faster for round parts. | Better for intricate 3D shapes. |
At CNCRUSH, we excel in both CNC Milled parts and CNC Turned parts, ensuring that every project benefits from the most suitable process.
5. Common Materials Used in CNC Precision Turning
CNC turning is compatible with a variety of metals and plastics, each suited for specific applications.
| Material | Key Properties | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Lightweight, corrosion-resistant | Automotive parts, aerospace components. |
| Steel | Strong, durable, wear-resistant | Machine tools, structural components. |
| Brass | Excellent machinability, conductivity | Electrical components, fittings. |
| Plastics (PEEK) | High strength-to-weight ratio, biocompatible | Medical implants, electronics. |
6. Applications of CNC Precision Turning Across Industries
CNC precision turning is a backbone of many industries, offering unmatched precision for metal and plastic parts.
| Industry | Example Applications |
|---|---|
| Automotive | Engine components, axles, bushings. |
| Medical | Surgical tools, implants, housings. |
| Aerospace | Landing gear parts, turbine shafts. |
| Machine Building | Gears, pulleys, fasteners. |
| Automation | Robotic arms, custom fittings. |
At CNCRUSH, our expertise spans these industries, ensuring every part meets industry-specific standards.
7. The Role of Automation in CNC precision Turning
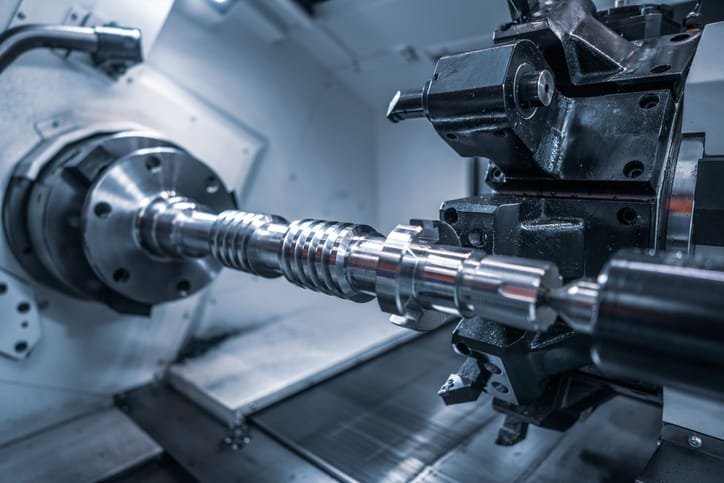

Automation has transformed CNC-turned, enabling high-volume production with exceptional consistency.
Key Benefits of Automated CNC Turning:
- Lights-Out Manufacturing: Machines operate 24/7 with minimal supervision.
- Faster Turnaround Times: Ideal for large production runs.
- Improved Quality: Eliminates variability caused by human error.
8. Achieving Superior Surface Finishes with CNC Turning
The surface finish of a turned part impacts its functionality, aesthetics, and durability.
| Finish Type | Typical Roughness (Ra) | Application |
|---|---|---|
| Polished | <0.2 µm | Medical implants, optical components. |
| Smooth Machined | 0.4–0.8 µm | Automotive shafts, gears. |
| As-Turned | 1.6–3.2 µm | General-purpose mechanical parts. |
💡 At CNCRUSH: We offer tailored finishing options to meet your specific requirements, ensuring high-quality results every time.
9. Challenges in CNC Turning and How to Overcome Them
Even advanced CNC-turned processes come with challenges, such as:
- Material Deformation: Avoid by selecting appropriate feeds and speeds.
- Tool Wear: Use high-quality tools and monitor wear rates.
- Thermal Expansion: Implement coolant systems to maintain part integrity.
By leveraging 12 years of experience, CNCRUSH excels in tackling these challenges for seamless production.
10. The Future of CNC Turning
With advancements in automation, AI-driven machining, and hybrid manufacturing, CNC turning is poised for even greater versatility and precision.
💡 Future Trends to Watch:
- Digital Twins: Real-time simulation of machining operations.
- AI Integration: Predictive maintenance and process optimization.
- Hybrid Machines: Combining CNC turning with additive manufacturing.
At CNCRUSH, we continually invest in cutting-edge technologies to remain at the forefront of innovation.
FAQs: CNC Turning Basics
1. What is CNC turning used for?
CNC turning is used to produce cylindrical components like shafts, bushings, and screws.
2. How is CNC turning different from CNC milling?
CNC turning rotates the workpiece, while CNC milling rotates the cutting tool to shape stationary material.
3. Which industries benefit most from CNC turning?
Industries such as automotive, medical, aerospace, and automation rely heavily on CNC-turned precision parts.
Why Choose CNCRUSH for CNC Turning Services?
At CNCRUSH, we combine state-of-the-art machinery with experienced craftsmanship to deliver exceptional CNC machining services. With a focus on CNC Milled parts, CNC Turned parts, and custom solutions, we cater to industries like automotive, machine building, and automation.
👉 Contact us today to learn how we can bring precision, reliability, and affordability to your next project!
